What is software validation?
By Mitch on Friday, 2 November 2012, 14:11 - Processes - Permalink
Following the article about software verification, let's see what software validation is.
Validation after verification
If you've read the other article this is no news for you that the end of validation happens after the end of verification.
In fact, validating a device is ensuring that it conforms to defined user needs and intended uses. In the light of this definition, verification is a part of the whole process of validation.
Before ensuring that it conforms to user needs, the functions of the device have to be:
- described with software requirements and architecture,
- implemented with code,
- and tested.
So the requirements and the architecture have to be validated before they're implemented. That's why there are reviews of requirements, general conception and detailed conception before verification. These reviews participate to the validation process.
When requirements and architecture are validated, the software is implemented and tested through verification.
However verification tests as they are required by the IEC 62304 standard are not enough. Specific tests, i.e. clinical tests or end-user tests in real conditions, can be done to validate the device. So yes, some activities of validation happen after verification.
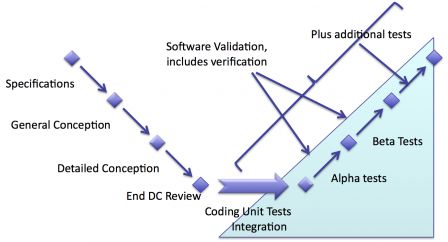
Goals of validation
The goals of validation are not purely technical, compared to those of verification. Validation shall answer these questions:
- Does software conform to its intended use?
- Is clinical use effective and efficient?
- Are risks mitigated?
- Is the risk / benefit ratio favorable?
- Are the requirements enforced by national regulations met?
Knowing these goals, it's easy to see that pure technical tests done on a tests platform are not enough.
Who does Validation tests
Since validation tests are not pure technical tests, it's the role of physicians, people with clinical knowledge to do validation tests. For this reason, validation tests are done in real environment, i.e. in healthcare centers.
Software teams don't do validation tests but they support them. If there is a bug a problem with software during validation, it's the role of software developers to find out what's wrong. And fix it!
Activities done for validation
Let's see what activities are required after the verification to complete the validation.
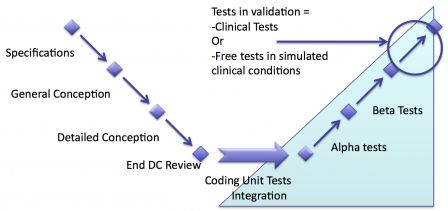
Clinical tests
The most obvious type of activity is clinical tests. From the point of view of IEC 62304, supplying software for clinical tests is equivalent to delivering software to end-users. Thus clinical tests are the beginning of software maintenance regarding IEC 62304.
Practically, the technical conditions in which software is used in clinical tests can be very close those of verification. Especially for standalone software: an end-user with clinical knowledge tests software on a PC.
The first main difference is the testing protocol, which, for clinical tests is highly formalized. The second main difference is the use of software with real patients. This is not 100% true, though, with standalone software. Standalone software can be tested with real data sets that were archived even before software was designed.
No clinical tests
Depending on the regulations in the countries where software will be sold, clinical tests may not be necessary. Usually software, which already have an equivalent on the market can be validated with existing clinical data.
In this case there are no clinical tests. Software testing either stops after the end of verification, or finishes by a last phase of free tests in simulated clinical conditions.
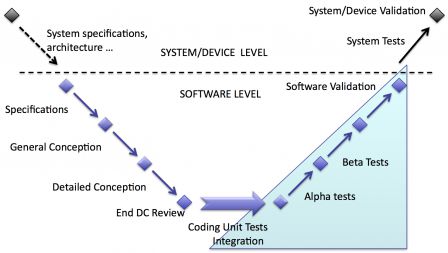
Software validation and Device validation
When software is embedded in a device, there may be two types of validation:
- software validation: validation of software only,
- device validation: validation of the device with software inside.
So, there may be only one validation of the whole device or two validations: one for software and one for the device. It depends deeply on the type and complexity of software embedded in the device.
If the functions ensured by software are very complex and/or critical, a separate validation of software may be deemed necessary. Separating software validation is a way to reduce the complexity of the validation of the whole device.
Validation review
The validation ends with a validation review with people who participated to the design, the verification tests, and the validation tests. An "independent reviewer" (someone who didn't participate to design and validation tasks) may also be required by some national regulations. The purpose of the validation review is ensuring that all goals enumerated above are met:
- software conforms to its intended use,
- clinical use is effective and efficient,
- risks are mitigated,
- the risk / benefit ratio is favorable,
- the requirements enforced by national regulations are met.
For embedded software, there may be two validation reviews, if software is validated separately before the whole device.
The validation review marks the end of the whole process of validation. Usually people use the word "validation" with both meanings: the big validation process or the validation review. The validation review is the successful end of efforts stretched on months or years. Thus some people think of validation with the meaning of validation review.
When software is validated, the phase of maintenance begins. But this is another story I'll tell in another article!

Comments
I like the way and the concept of this article.
However in my universe I am having a more holistic view and every activity fall into the scope of the validation, as long as we do that for the purpose of ensuring the fulfilments of the intended use. Having said that, it includes configuration management, risk management, project management, verification, reviews, etc.
But it is only about semantics.